Eczema, a prevalent and non-contagious skin condition, manifests as dry and itchy patches on the skin. While it can significantly impact quality of life, its symptoms often worsen upon exposure to irritants or allergens. Although there is no cure for eczema, various treatments can effectively help manage and alleviate its symptoms.
Overview
What is Eczema?
Eczema is a skin condition that causes your skin to become dry, itchy, and bumpy. This condition weakens your skin’s barrier function, which is responsible for helping your skin retain moisture and protecting your body from outside elements. Eczema is a type of dermatitis, which is a group of conditions that cause skin inflammation.
Types of Eczema?
There are several types of eczema, each with unique triggers that can affect your skin’s barrier function, including:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common type, often associated with other allergic conditions like asthma and hay fever.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by direct contact with irritants or allergens.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the edges of the fingers, toes, palms, and soles.
- Neurodermatitis: Involves thick, scaly patches on the skin due to repeated scratching.
- Nummular Eczema: Presents as round, coin-shaped spots on the skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Causes scaly patches, red skin, and stubborn dandruff, typically affecting oily areas.
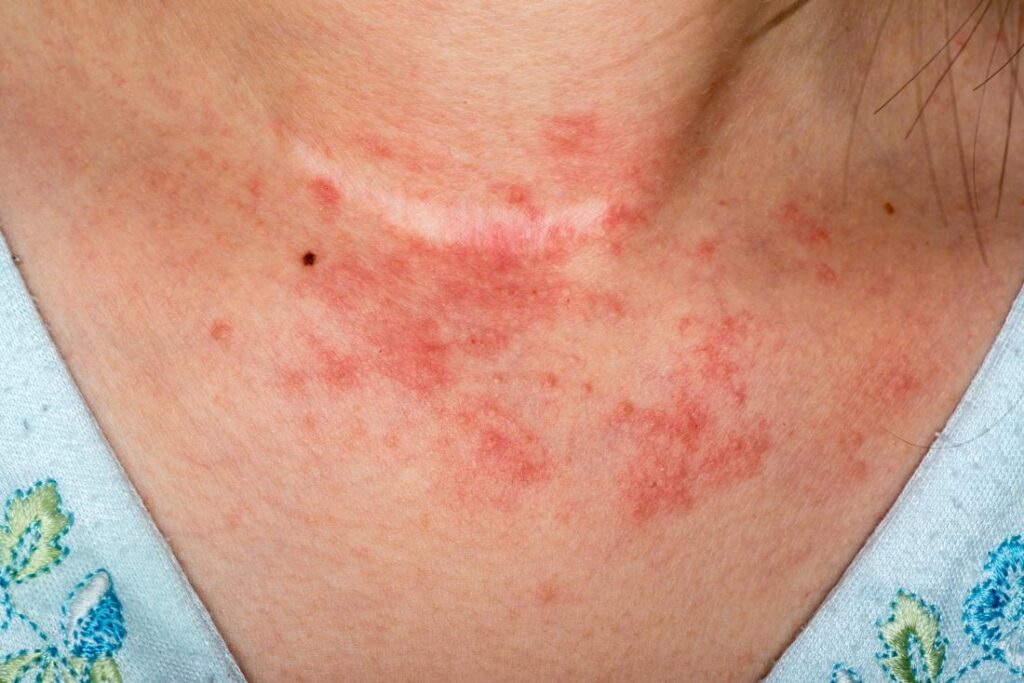
It’s possible to have more than one type of eczema at the same time. Eczema is a common condition affecting over 31 million Americans. Its primary symptoms include itchiness, rashes, dry patches, and potential infection. The condition often involves extreme itchiness, and scratching can worsen the symptoms. Flare-ups, when symptoms are at their worst, can last for days or even weeks.
Eczema Symptoms
Eczema can look different for everyone, and flare-ups won’t always occur in the same area. Regardless of the affected area, eczema is almost always itchy, sometimes even before a rash appears. Additional symptoms include:
- Redness
- Dry and cracked skin
- Swelling with a rash (color varies depending on skin color)
- Bumpiness (especially on brown or Black skin)
- Thick and leathery patches
- Oozing and crusting
- Raw skin from scratching
These symptoms can vary in severity and may affect different parts of the body during different flare-ups.
Does Eczema Affect people at a certain age?
Eczema can affect individuals of any age, although symptoms typically manifest during childhood and may persist into adulthood. You may be more prone to developing eczema if you have a family history or a diagnosis of:
- Dermatitis
- Allergies
- Hay fever
- Asthma
What Causes Eczema to Develop?
The initial signs of eczema include itchiness, dry skin, and a rash. These symptoms often indicate exposure to an environmental trigger that has caused the condition to start or flare up. Identifying and avoiding these environmental triggers can help reduce the risk of future eczema flare-ups.
Is Eczema transmittable?
No, eczema is not contagious. You cannot catch eczema from someone else, nor can you pass it on to others.
Eczema Risk Factors
Several factors can increase the risk of developing eczema, with stress and genetics being among the most common. Additional risk factors include:
- Having very dry skin
- Using hair care or skin products with certain allergens
- Having food allergies
- Living in cold, damp areas or in swampy, hot areas
- Having a family history of eczema
Age can also influence the likelihood of developing eczema:
- Eczema often appears before the age of 5, with many children outgrowing the condition.
- In adults, eczema is more likely to develop either in their 20s or after age 50.
- Atopic dermatitis is more common in children, whereas forms like nummular eczema are more typical in adults.
Eczema Treatment
The primary goal of eczema treatment is to alleviate and prevent itching, which can lead to infection.
Medications
- Corticosteroid Creams and Ointments: Your doctor may prescribe these to reduce inflammation.
- Antibiotics: If the affected area becomes infected, antibiotics may be necessary.
- Tar Treatments: These chemicals help reduce itching.
- Phototherapy: This treatment involves using ultraviolet light to manage symptoms.
- Cyclosporine: An immunosuppressive drug used in more severe cases.
The FDA has also approved two medications known as topical immunomodulators (TIMs) for mild to moderate eczema:
- Elidel Cream
- Protopic Ointment
These medications work by altering your immune system’s response to prevent flare-ups, reducing inflammation, and alleviating itching.
Eczema Skincare Products
Proper skincare is essential in managing eczema and preventing flare-ups. Here are some recommended types of products:
Moisturizers

Purpose: Hydrate and protect the skin’s barrier.
- Emollients: Thick creams or ointments like CeraVe, Eucerin, or Aquaphor.
- Humectants: Products containing glycerin or hyaluronic acid.
Cleansers
Purpose: Cleanse without stripping the skin of natural oils.

- Gentle Cleansers: Cetaphil Gentle Skin Cleanser or Aveeno Daily Moisturizing Body Wash.
- Soap-Free Options: Free from harsh chemicals and fragrances.
Anti-Itch Creams
Purpose: Relieve itching and prevent scratching.
- Hydrocortisone Cream: Over-the-counter options like Cortizone-10.

- Calamine Lotion: To soothe irritated skin.
Barrier Repair Creams
Purpose: Restore the skin’s natural barrier.
- Ceramide-Containing Products: CeraVe Moisturizing Cream.
- Prescription Options: Such as Epiceram.
Bath Treatments
Purpose: Soothe and hydrate the skin during bathing.
- Oatmeal Baths: Aveeno Soothing Bath Treatment.
- Bath Oils: Eucerin Skin Calming Bath Treatment.
Specialty Products
Purpose: Address specific needs or severe cases.
- Topical Immunomodulators: Prescription options like Elidel or Protopic.
- Antimicrobial Products: For areas prone to infection.
When choosing skincare products for eczema, it’s important to avoid those with fragrances, dyes, and harsh chemicals. Always patch-test new products and consult with a healthcare provider for personalized recommendations.
