What is Scabies?
Scabies is a highly contagious skin condition caused by the Sarcoptes scabiei var. hominis mite, also known as the human itch mite. It affects around 200 million people globally at any one time, impacting individuals of all ages, races, and socioeconomic statuses. Scabies spreads easily through close physical contact and the sharing of infested items like bedding, clothing, and furniture.
Can You Get Scabies from Animals?
Humans cannot contract the type of scabies that commonly affects animals. A different type of mite causes scabies in pets, leading to a condition called mange. While mange can affect people, it is caused by a different mite species than human scabies.
Types of Scabies
The scabies mite that infests humans can lead to several types of infestations:
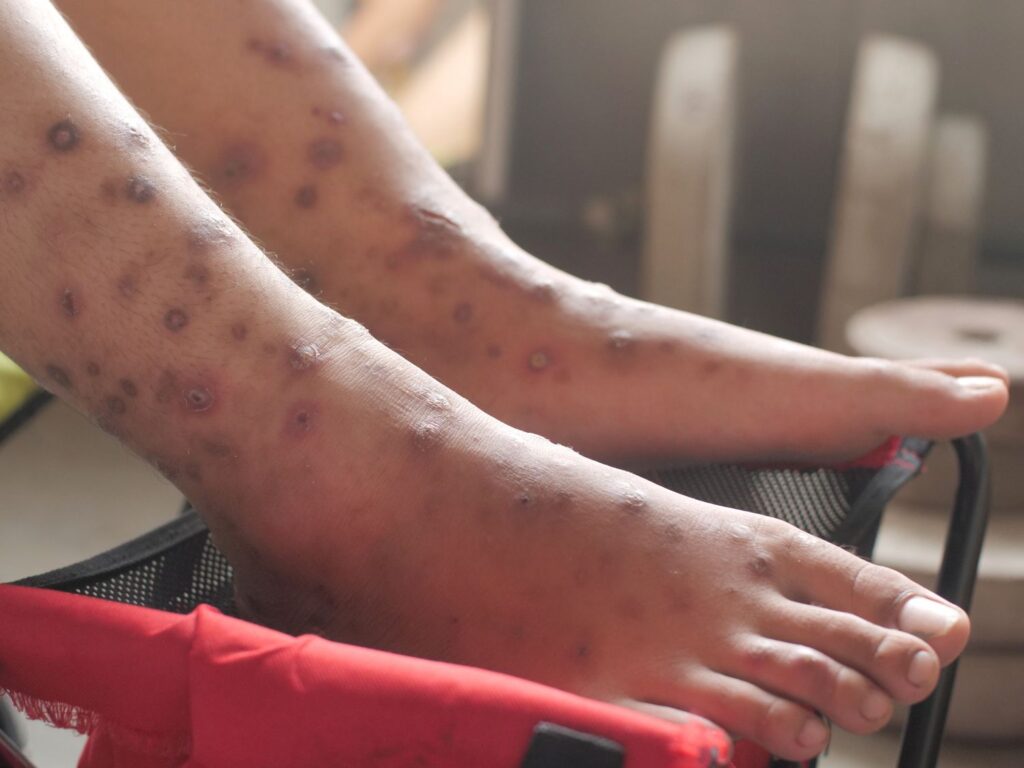
- Typical Scabies: The most common form, characterized by an itchy rash typically appearing on the hands, wrists, and other common areas.
- Nodular Scabies: This form presents as itchy, raised bumps or lumps, particularly around the genitals, armpits, or groin.
- Norwegian (Crusted) Scabies: A severe and extremely contagious type of scabies. People with crusted scabies develop thick skin crusts containing thousands of mites and eggs. This condition can be life-threatening and requires immediate medical attention.
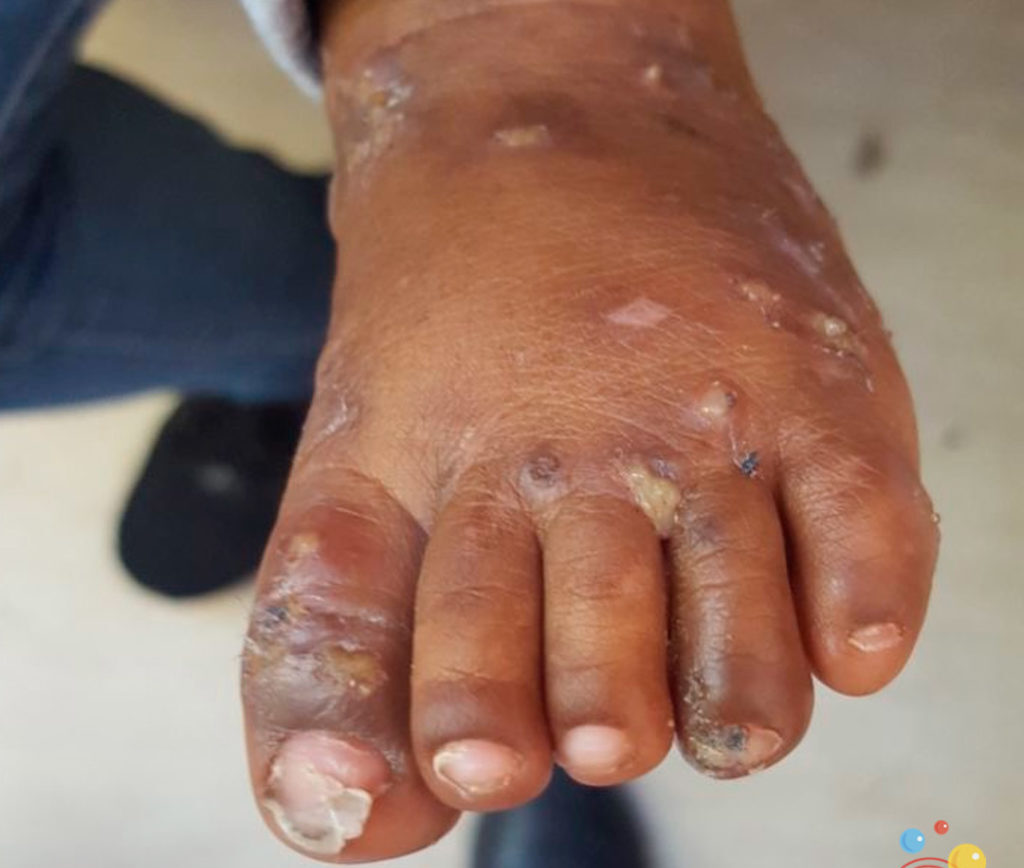
What Does Scabies Look Like?
Scabies results in discolored rashes where mites burrow into the skin. These patches can appear scaly and include bumps and blisters. Severe infestations may lead to heavy crusting.
Crusted Scabies Symptoms
Crusted scabies, also known as Norwegian scabies, presents more severe symptoms compared to regular scabies. While some individuals may only experience crusting, others can have a range of intense symptoms:
- Intense Itching: Severe itching that often disrupts sleep.
- Hive-like Bumps: Raised, hive-like bumps on the skin.
- Scaly, Crusty Rash: Thick, scaly, and crusty patches on the skin.
- Sores: Sores that can result from intense scratching, which may lead to secondary infections.
Characteristics of Crusted Scabies:
- Thick Crusts: Individuals with crusted scabies have very thick crusts on their skin due to the large number of mites present.
- Common Infestation Sites:
- Arms
- Hands, especially between the fingers
- Buttocks
- Genitals
- Nipple area
- Waist area
- Skin covered by clothing or jewelry
Onset of Symptoms:
- Initial Infestation: If you’ve never had scabies before, it can take up to eight weeks for symptoms to appear after close contact with an infected person.
- Recurrent Infestation: If you have had scabies previously, symptoms may develop more quickly upon re-exposure.
Key Points:
- Highly Contagious: Close contact with someone who has scabies can lead to infestation.
- Severity: Symptoms are more intense in crusted scabies due to the higher mite count.
- Delayed Symptoms: Initial infestations may have a delayed onset of symptoms.
If you suspect you have crusted scabies, seek medical attention promptly to avoid complications and to receive appropriate treatment.
Common Infestation Sites
- Adults and Older Children: Between the fingers, around the fingernails, armpits, waistline, and inner wrists.
- Infants and Young Children: Scalp, face, neck, palms, and soles.
Duration and Types of Scabies
- Duration: Mites can live for 1-2 months on humans and up to 72 hours off the host.
- Types:
- Typical Scabies: Causes itchiness on hands, wrists, and other areas but not the face or scalp.
- Nodular Scabies: Results in itchy, raised bumps in areas like armpits and genital regions.
- Crusted Scabies: A severe form in individuals with weakened immune systems, marked by thick crusts.
Causes and Risk Factors
Scabies is caused by the infestation of the Sarcoptes scabiei mite, which burrows under the skin to lay eggs. It’s highly contagious and spreads through direct physical contact. Those at higher risk include children, caregivers, sexually active young adults, and people with weakened immune systems.
Treatment Options

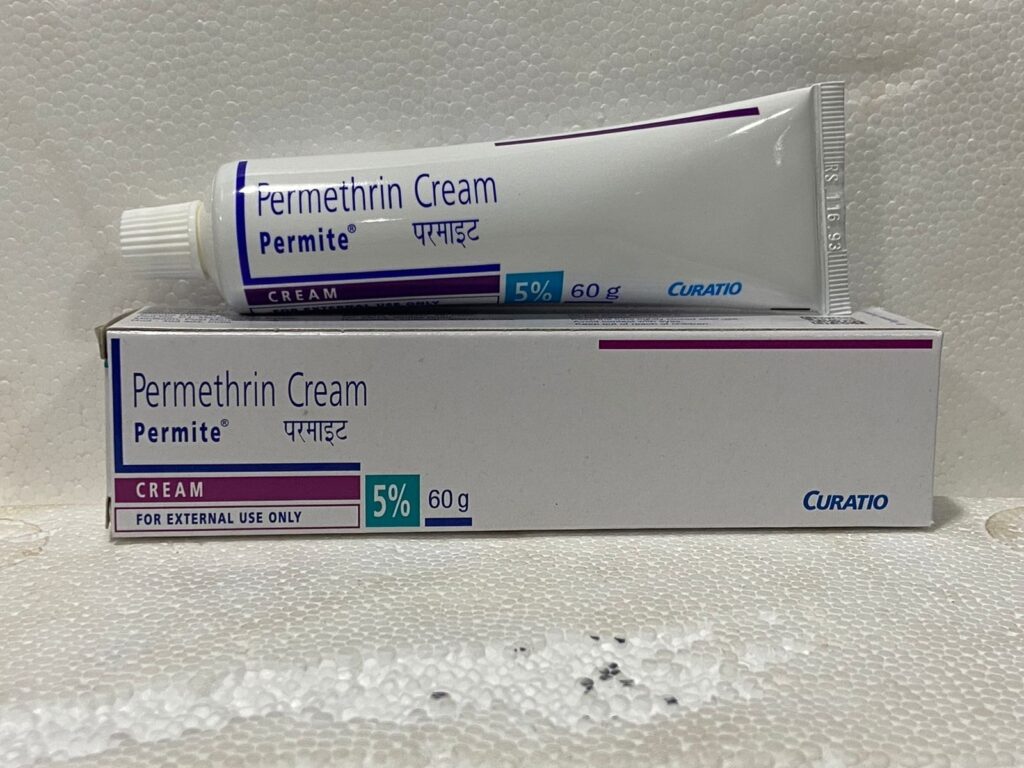
- Medications:
- Topical: 5% permethrin cream, crotamiton cream, lindane lotion, benzyl benzoate lotion, and sulfur ointment.
- Oral: Ivermectin for severe cases or those who do not respond to topical treatments.
- Additional Medications: Antihistamines, anti-itch lotions, antibiotics, and steroid creams to relieve symptoms.
Home Remedies
- Tea Tree Oil: May relieve itching and destroy mites.
- Oatmeal Bath: Soothes itching.
- Moisturizer: Gentle, fragrance-free products may help.
- Loose-Fitting Clothing: Prevents irritation.
Complications
Scratching can lead to skin sores, which may become infected, leading to serious conditions like heart disease, kidney disease, or blood poisoning.
Prevention
- Avoid Close Contact: Limit skin contact with infected individuals.
- Wash and Clean: Use hot, soapy water to wash clothes, towels, and linens. Dry on high heat. Vacuum carpets, rugs, and upholstery.
- Hygiene: Maintain cleanliness to prevent infestation.
Summary
Scabies is a contagious skin condition caused by microscopic mites. It results in itching and rashes and spreads through close contact. Treatment involves topical medications and home remedies, but prevention through limiting contact and thorough cleaning is crucial. Consult a healthcare provider before trying any home remedies.